Share Post:
To some, air conditioners are an absolute necessity today, yet very few people know how to fix overcharged AC. In an attempt to save some money, many car owners purchase inexpensive, faulty cans of coolants.
They then endeavor to recharge their ACs themselves. Applying some DIY skills to the situation is not the problem. The issue lies in the unreliable gauges included on the coolant.
When air conditioners become overcharged, the best thing to do is call the mechanic. If seeking a mechanic for a costly and untimely fix is not a feasible option, the other choice is to learn about discharging air conditioners at home.
The following article will assist those who choose to pursue either option.
How Do ACs Become Overcharged?
Young motorists, especially, are more likely to make the valiant effort to add refrigerants to their AC systems.
Particularly in summer, as the weather becomes warm, incidents of overcharged ACs are aplenty. These young persons must now seek out ways to fix overcharged AC.
A few things can cause an overcharged AC. However, the most common cause is an inexperienced young man (or woman) trying to top up the refrigerant in their car.
They possibly add too much to the system, which results in the AC becoming overcharged.
Not everyone adds too much refrigerant on purpose. Some people are unlucky enough to have purchased a bad can of coolant with an erroneous gauge.
The gauge sometimes reads incorrect pressures or completely freezes up, making it extremely difficult to read the levels of coolant being added to the system.
It is for this reason that the recommended route is to have a professional recharge the car AC.
Once an overcharge happens, the system no longer does as it is designed to do, blowing cool air. It now starts to release stiflingly hot air from the vents.
Signs and Symptoms of Overcharged Car AC
A properly working AC system should come on as soon as you press the button. If the vehicle was off for a while, AC starts up time may take one to two minutes.
Anything that falls outside of two minutes could indicate that the AC system is broken or getting there.
Before undertaking the task of ascertaining how to fix overcharged AC, one should take care to investigate. The investigation aims to verify whether or not the car AC has been overcharged.
There are a few things to consider when ascertaining whether or not the AC is overcharged.
01. Faulty Cooling
One of the most evident signs of an overcharged AC is faulty cooling. The vents may produce only slightly cooler air than room temperature, or they could just outright be blowing warm to hot air.
When faulty cooling in the air vents happens, the entire car is likely to experience overheating. Luckily this takes a long period of neglect to happen.
However, the issue presents itself; inadequate cooling is the most obvious symptom of an overcharged AC.
02. Noisy or Broken Compressor
The AC works in a cycle transforming compressed liquid coolant into a gas and then back to its liquid state. If the AC system is overcharged, the change from liquid to gas cannot happen, so the compressor starts producing liquid coolant instead of gas.
It now has to work extremely hard to pump the excess coolant through the lines. The result is a noisy or broken compressor.
The compressor starts to produce excessive noise as it fights to move the liquid refrigerant through a pipe originally intended for gas. However, loud noises from the compressor are not a sure thing.
Many motorists do not experience this sign. Some are even lucky enough to have AC system compressors with emergency structures that can prevent the destruction of the pump.
Others who do not have this system end up with a broken compressor over time.
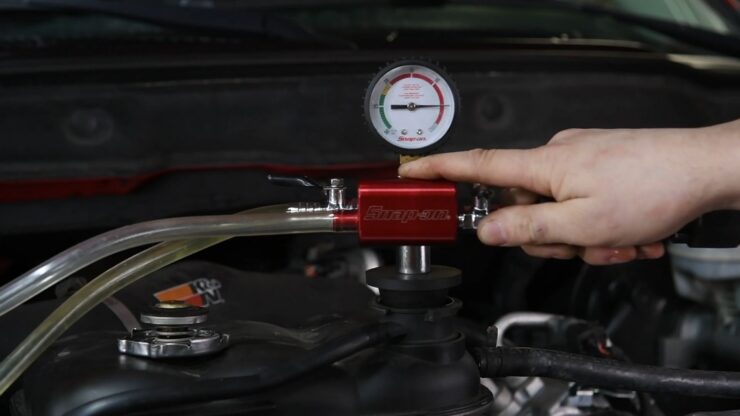
03. High Pressure
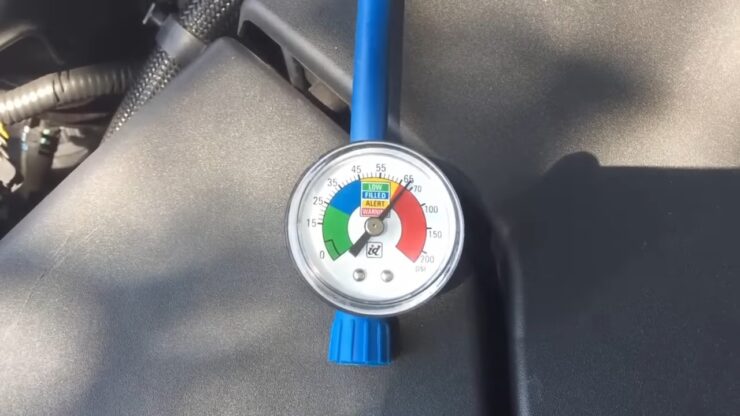
Every AC system comes with a pressure gauge. The system will alert you when that gauge has been filled past maximum capacity.
When the AC is overcharged, that pressure gauge reads higher pressures and temperatures than ordinary.
The compressor was not built to handle the excess coolant in the lines. Consequently, this raises the pressure, and the temperature heightens.
There is a feedback effect because as the temperature gets hotter, the pressure increases and vice versa.
04. Failing Engine
Like every other car component, the compressor draws a considerable amount of energy from the engine. Significant pressure is placed on the machine by the compressor trying to overcompensate for the steep levels of coolant added to the system.
The pressure accumulates, and you may start to notice sluggish movement and excessive loss of fuel from your vehicle.
How to Fix Overcharged AC in Car System
The first and most highly endorsed step to take with an overcharged AC is to have a mechanic look at it.
To preserve the compressor’s life, have a professional examine the car, especially if a novice had attempted to recharge the AC.
Since the overcharge was caused by adding too much coolant, the obvious fix is to remove some of that coolant from the lines.
This is a very simplified version of what needs to be done. The actual procedure is a little bit more complicated, so it is better left to a mechanic. The good thing about it is that it is not impossible to do.
01. See a Mechanic
Refrigerant is a dangerous chemical. It is advised that motorists seek auto professionals to remove some of the coolants from the system and return the AC to normal pressure.
These hazardous chemicals are so dangerous that specific laws govern what can be done to remove excess coolant.
Mechanics are aware of these best practices. A layperson will not know that there are things that they need to go over before they can even attempt to remove the coolant.
One instance of this is the fact that many people still refer to coolant as Freon. That is incorrect. Freon is now illegal and is no longer used to recharge AC systems.
How the Mechanic Fixes Overcharged AC?
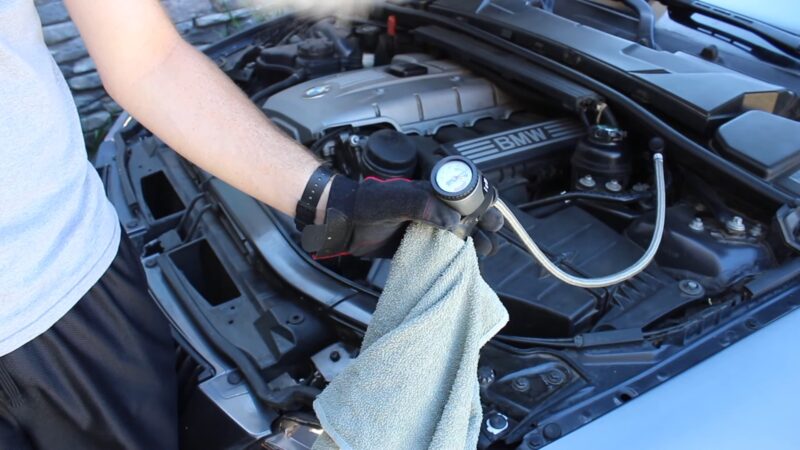
The mechanic uses a machine that incorporates airtight vacuums and seals to bleed the coolant from the AC. This equipment does all the work to remove the refrigerant safely.
The wonderful thing is that this is an enclosed system. It collects the coolant in a container for recycling or reuse later or in another car. Either way, it keeps the chemical out of the environment.
One end of the machine is attached to a high-pressure port and the other end to a low-pressure port. The mechanic uses a gauge to determine how much coolant is in the system based on the pressure readings.
The machine is then allowed to run until the pressure reading reflects the usual amount of refrigerant in the system.
Remember the feedback effect of high pressure yielding high temperatures in the AC system? Well, this feature works favorably in the discharge process.
As the pressure lowers, the temperature lowers; as the temperature decreases, this causes the pressure to fall in the system.
The lower pressure is the endgame here. The compressor will not work so hard to pump coolant through the lines and stress the entire system into malfunctioning.
Most mechanics charge from $200-$300 to recharge AC systems. Many of them charge slightly lower than that to discharge it.
The price is usually only lower because there is no actual purchase of coolant with this procedure. The expected cost for discharging an AC system is about $150 – $250. There may be slight differences in the price based on the car’s make, model, and year.
It may seem costly, but you will not need to risk life, limb, or liberty in the grand scheme of things if the procedure is done by a professional.
02. DIY Options
Sadly, there are no DIY options for discharging a car AC. No legal ones, at least. This is due to the many laws surrounding the removal and disposal of harmful chemical coolants.
To legally drain the excess coolant from an AC system, one would have to be certified.
Cause of Overcharged AC in Car
An overcharged car AC is due to the improper addition of coolant. Coolant is the liquid substance added to the lines of a vehicle’s AC system to recharge it. It is also the reason why
AC systems become overcharged. The issue does not lie in using or changing coolant; it surrounds the misuse of the substance by people who are not mechanics trying to recharge their systems at home.
01. Faulty Gauge Attached to Store-bought Coolant
Non-professionals tend to overcharge their systems. This is due to a higher likelihood of using cheaper, generic coolants and the often-faulty gauges attached.
There is an incredibly high chance of adding more coolant with an erroneous gauge than the system can handle.
02. Not Knowing How Many Coolants to Add
These motorists could also be adding too much coolant because they do not know how much their specific car brand, model, and year can take.
Watching a few YouTube videos is not adequate research to provide the knowledge needed to recharge an AC system at home. Sadly, this is what many people do, and the result is an overcharged AC system.
03. Adding the Wrong Coolant
They also probably have not considered the fact that not all coolants are created equal. Some coolants, like any other retail product, do not work how they are supposed to.
There is also the fact that most cars have a specific coolant they can take. The introduction of a refrigerant not meant to be in the system can also result in an AC overcharge.
Prevention of Overcharged AC
The primary way to not overcharge the AC is to allow a professional mechanic to recharge it in the first place.
However, if that option is not available, there are some things to consider before recharging the AC.
01. Get a Good Gauge
Most coolants come with a gauge attached. To ensure that there is no chance of overcharging the AC, purchase a good gauge from a dependable brand.
Make sure to do your research about it and use it to test the system’s pressure every day for a few days before you try adding coolant.
02. Know More About the Car
Know what coolants work best for your vehicle. Read the car manual for guidance. It is also important to note the proper measurements of coolant that the car can handle.
03. Take the Car to a Mechanic
This is the safest option and is heavily recommended. Home accidents happen even without the participation of dangerous chemicals like coolants.
Allow the matter to be looked after by a professional with all the technical know-how and equipment.
Do’s and Don’ts
Do’s
- Take the car to a mechanic to fix overcharged AC.
- Learn more about your vehicle before attempting to recharge its AC.
- Use good gauges when adding coolant at home.
Don’ts
- Attempt to discharge AC at home.
- Handle coolant without safety gear.
- Handle coolant at all if possible.
- Use bad or flat-out wrong coolant in your AC system.
Common FAQs
Please turn on the car and put it in the park. Then activate the emergency brake. Power up the AC and use your pressure gauge to connect to the low side of the compressor.
Add a couple of ounces of coolant. If you hear a click and some humming, the compressor is on. (if it does not turn on, check the fuses)
The gauge should read 38 lbs per square inch (aka the blue zone). Any other readings or the compressor not turning on indicate that you may need a new compressor.
Too much or not enough refrigerant causes an icy build-up while simultaneously destroying the compressor.
In other words, overcharged AC can cause a frozen compressor and, consequently, iced up AC.
Readings may vary based on the outside temperature. The low side should ideally be about 30 PSI at 90 degrees Fahrenheit or a little less than that.
The high side should be about twice the room temperature plus 50 PSI.
Here are a few tips to increase the car AC performance:
– Change the filter regularly and keep it clean.
– Ensure that the refrigerant is adequately topped up and not leaking
– Do not start the AC until you start driving.
To prevent overcharging your car’s AC system, you should:
- Take your car to a professional mechanic for AC recharging
- Use a reliable gauge if recharging at home
- Research and use the correct type of refrigerant for your car
- Learn about your car’s specific AC system requirements (from the owner’s manual or a certified mechanic)Can an overcharged AC cause my car’s engine to fail?
An overcharged AC can put extra strain on the engine, leading to sluggish performance and excessive fuel consumption. However, it is unlikely to cause complete engine failure unless the issue is left unresolved for an extended period.
Verdict
Coolants are hazardous chemicals and should be handled by a professional and with extreme caution. They are the reason why trying to fix an overcharged AC is so tricky.
It is necessary to remove excess coolant to discharge the AC, and the process cannot be done at home.
While it is easy and legal to purchase coolants and add them to the AC system at home, only certified professionals can remove coolants.
This is because of the dangers the chemical poses to a person’s health and the environment.
For more maintenance and repair tips, check here!
Related Posts:
- How to Track Your Car's Mileage - A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Reset Maintenance Light on Toyota Tundra -…
- Diesel vs. Gas Trucks - Which Has More Mechanical…
- Can Electric Trucks Handle the Heavy Lifting? A Look…
- When Will Entry-Level Electric Trucks Hit the Market?
- Trac Off Light - What It Means and How to Fix It